This function takes SBML files as input, and returns either a metabolic or a signaling network as output.
SBML2igraph(
filename,
parse.as = c("metabolic", "signaling"),
miriam.attr = "all",
gene.attr,
expand.complexes,
verbose = TRUE
)Arguments
- filename
A character vector containing the SBML files to be processed. If a directory path is provided, all *.xml and *.sbml files in it and its subdirectories are included.
- parse.as
Whether to process file into a metabolic or a signaling network.
- miriam.attr
A list of annotation attributes to be extracted. If
"all", then all attibutes written in MIRIAM guidelines (see Details) are extracted (Default). If"none", then no attributes are extracted. Otherwise, only attributes matching those specified are extracted.- gene.attr
An attribute to distinguish
speciesrepresenting genes from those representing small molecules (see Details). Ignored ifparse.as="metabolic".- expand.complexes
Split protein complexes into individual gene nodes. Ignored if
parse.as="metabolic", or whengene.attris not provided.- verbose
Whether to display the progress of the function.
Value
An igraph object, representing a metbolic or a signaling network.
Details
Users can specify whether files are processes as metabolic or signaling networks.
Metabolic networks are given as bipartite graphs, where metabolites and reactions represent
vertex types. This is constructed from ListOfReactions in SBML file, connecting them
to their corresponding substrates and products (ListOfSpecies). Each reaction vertex has genes attribute,
listing all modifiers of this reaction. As a general rule, reactions inherit all annotation
attributes of its catalyzig genes.
Signaling network have genes as vertices and edges represent interactions. Since SBML format may
represent singling events as reaction, all species are assumed to be genes (rather than small
molecules). For a simple path S0 -> R1 -> S1, in signaling network, the path will be
S0 -> M(R1) -> S1 where M(R1) is R1 modifier(s). To ditiguish gene species from small
molecules, user can provide gene.attr (for example: miriam.uniprot or miriam.ncbigene)
where only annotated species are considered genes.
All annotation attributes written according to MIRIAM guidlines (either urn:miriam:xxx:xxx or
http://identifiers.org/xxx/xxx) are etxracted by default. Non-conforming attributes can be extracted
by specifying miriam.attr.
To generate a genome scale network, simply provide a list of files to be parsed, or put all
file in a directory, as pass the directory path as filename
Note: This function requires libSBML installed (Please see the installation instructions in the Vignette). Some SBML level-3 files may requires additional libraries also (An infomative error will be displayed when parsing such files). Please visit http://sbml.org/Documents/Specifications/SBML_Level_3/Packages for more information.
See also
Other Database extraction methods:
KGML2igraph(),
biopax2igraph()
Examples
if(is.loaded("readsbmlfile")){ # This is false if libSBML wasn't available at installation.
filename <- system.file("extdata", "porphyrin.sbml", package="NetPathMiner")
# Process SBML file as a metabolic network
g <- SBML2igraph(filename)
plotNetwork(g)
# Process SBML file as a signaling network
g <- SBML2igraph(filename, parse.as="signaling",
gene.attr="miriam.uniprot",expand.complexes=TRUE)
dev.new()
plotNetwork(g)
}
#> Parsing SBML files as metabolic networks
#> Processing SBML file: /__w/_temp/Library/NetPathMiner/extdata/porphyrin.sbml, SBML level 2 version 4: 19 reactions found.
#> SBML files processed successfully
#> Constructing Metabolic Network
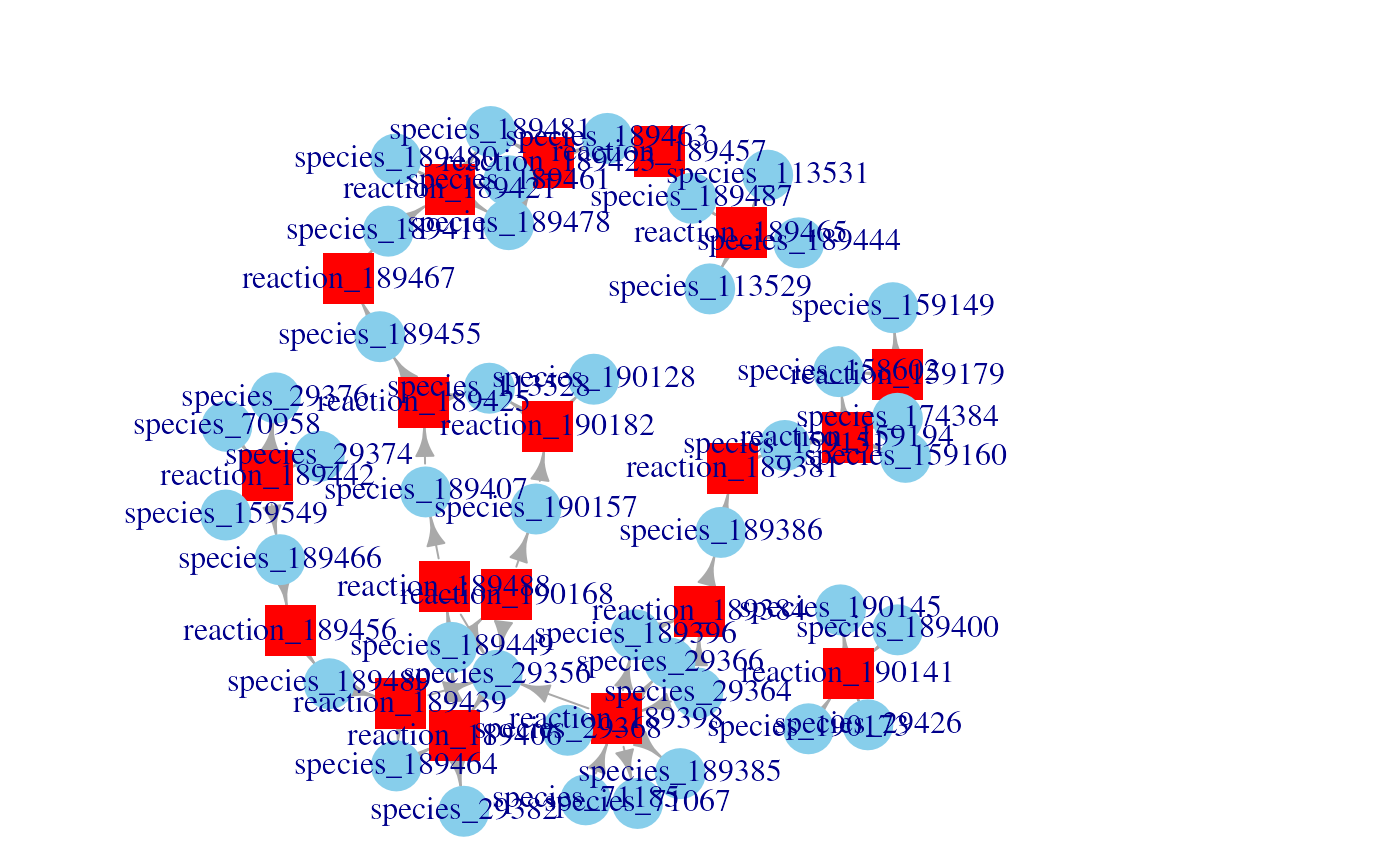 #> Parsing SBML files as signaling networks
#> Processing SBML file: /__w/_temp/Library/NetPathMiner/extdata/porphyrin.sbml, SBML level 2 version 4: 19 reactions found.
#> SBML files processed successfully
#> Parsing SBML files as signaling networks
#> Processing SBML file: /__w/_temp/Library/NetPathMiner/extdata/porphyrin.sbml, SBML level 2 version 4: 19 reactions found.
#> SBML files processed successfully